There is no point of doing the rest of your routine without sunscreen and most people find that simply introducing sunscreen helps to alleviate skin concerns such as hyperpigmentation and skin barrier damage.
What is sunscreen?
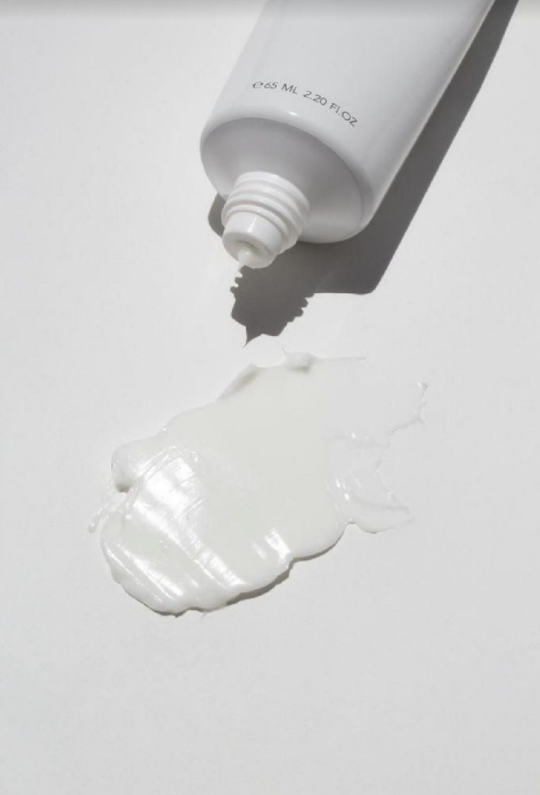
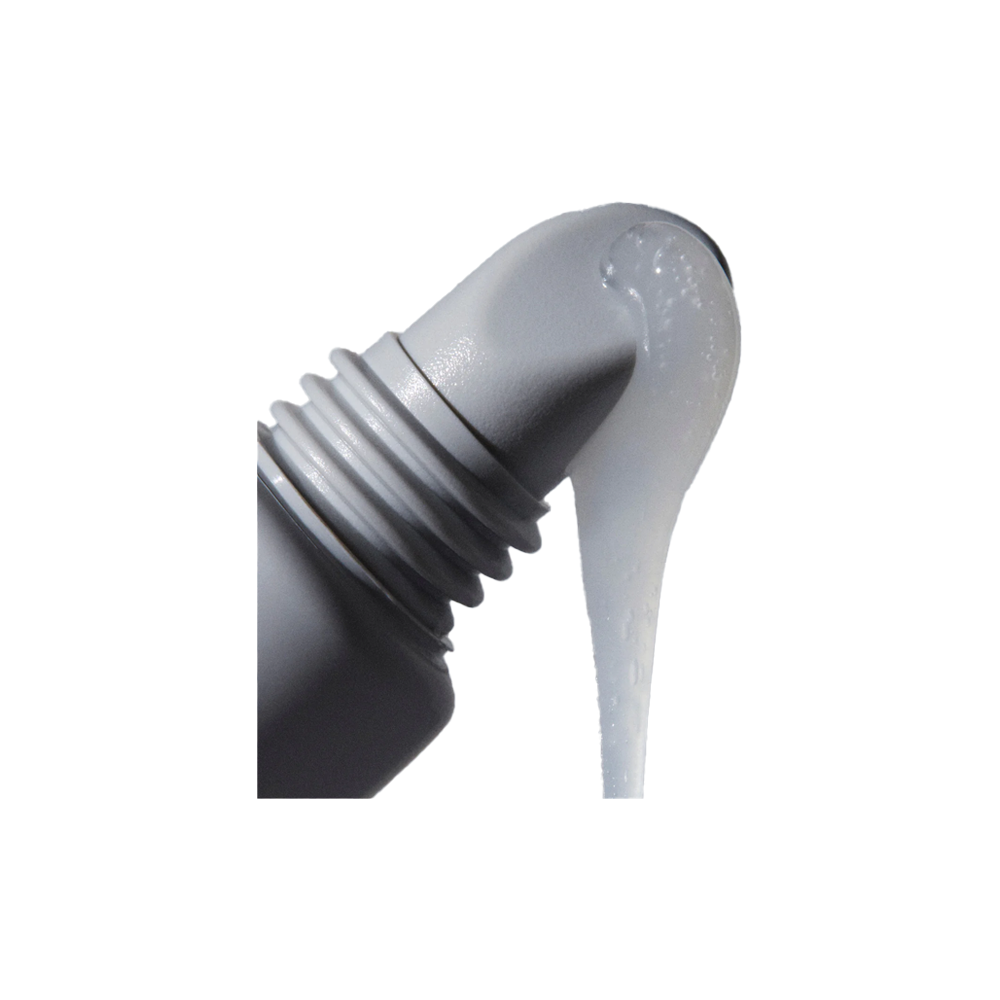
Sunscreen or SPF is a product that is applied to the skin to block out UVA and UVB ray. We are all used to traditional sunscreens that come in cream format, but the market has since expanded to sunscreen sprays, oils and gels to suit your preference.
What type of sunscreen works best for you?
If you have been the victim of a super white cast then you’ve probably tried a mineral sunscreen which uses the SPF filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. Both of those ingredients are white powders that will always leave a cast no matter how good the formula is. If you would like a cast free sunscreen experience, your best bet will be using a chemical sunscreen, which uses filters such as avobenzone.
How much sunscreen should you apply?
Sunscreen application is very precise, you cannot apply less if you do not like the texture or finish of a sunscreen. Scientifically speaking it is advised to apply 2mg of sunscreen per centimeter squared of skin, this is often equated to ¼ of a teaspoon for the face and an entire shot glass for the rest of your body. In order to achieve the SPF rating as displayed on the bottle, you must apply the full suggested amount.
How often should you apply sunscreen?
Your sunscreen is always the last product to be applied in your skincare routine, as it needs to create a film that acts as a shield from UVA and UVB rays. This film gets broken down throughout the day by sweat, oils and touch which is why sunscreens must be reapplied every two hours to maintain adequate protection.
What is the difference between UVA and UVB rays?
UVA rays are longer in wavelength and are linked to premature skin aging, whilst UVB rays are shorter in length and are responsible for skin burning. Both types of UV rays contribute to skin damage and DNA damage which increases the risk of some skin cancer.
The big C, let’s talk about skin cancer
Not all skin cancers are directly related to sun exposure, but the two main forms of melanomas that are linked to sun exposure are basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Any form of cancer is a cause for concern, but skin cancer affects one in five Americans, with increased numbers in sunnier climates. Whilst skin cancer is easier to identify and treat, than other forms of cancers. It is important to check your skin regularly for any new moles or irregularities in pre-existing moles.